What Are Entities in SEO? A Comprehensive Guide
SEO has evolved far beyond just keywords. While keywords still play a role, search engines now rely on entities to better understand the context and intent behind search queries. As Brooks Manley notes on Search Engine Watch, “Keywords aren’t dead, but entities give better insight to search engines on the relationship between words in a search.”
Entities are identifiable concepts such as people, places, organizations, and things that search engines recognize and connect with relevant information. Google’s Knowledge Graph and entity-based SEO refine search results by categorizing entities, capturing semantic relationships, and improving contextual relevance. This shift allows search engines to move beyond just keywords and deliver more accurate search results.
But how do website owners optimize for entities? And what role do structured data and semantic search play in improving search performance? Let’s find out how entity SEO is transforming the way Google recognizes and ranks content.
What Are Entities in SEO?
Entities in SEO refer to distinct, well-defined concepts that search engines recognize and use to understand the context within search queries.
Unlike keywords, which are just strings of text, entities represent real-world objects such as people, places, organizations, and ideas. These are not limited to words but are instead recognized as structured data that search engines can categorize, connect, and reference.
When Google’s Knowledge Graph processes search queries, it doesn’t just match relevant keywords; it maps out relationships between different entities to deliver more precise search results.
For example, if a user searches for “Einstein,” search engines don’t just look for pages containing the word “Einstein.”
Instead, they identify Albert Einstein as an entity and pull relevant information from sources like his Wikipedia page, news articles, and other entity databases. This structured approach helps Google recognize connections between concepts, improving search performance by delivering accurate search results instead of just keyword-based matches.
One of the most visible ways entities appear in search results is through the Knowledge Panel, which displays key details about specific entities pulled from Google’s Knowledge Graph. This highlights how entity-based SEO is not just about ranking content but about providing contextual relevance that aligns with user intent.
By focusing on entity optimization, website owners can make it easier for search engines to understand their content. This involves more than just using keywords; it includes using structured data, schema markup, and internal linking to help search engines recognize semantic relationships and boost visibility in relevant search results.
The Importance of Entities in Modern SEO
SEO is no longer just about keyword placement—search engines now emphasize understanding concepts and relationships rather than simply matching words. Previously, exact-match keywords dominated optimization strategies, but advancements in natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning have shifted the focus toward entities and their connections.
This allows Google’s Knowledge Graph to refine search results by identifying real-world entities and their relevance, rather than relying on repetitive keyword usage.
Entity-based SEO improves search relevance by helping search engines understand content more holistically. Instead of treating a phrase as a collection of individual words, search engines analyze how entities connect to determine meaning. For example, a search for “Apple” could refer to the tech company or the fruit, and Google recognizes the distinction based on search intent and semantic relationships between different topics.
This shift doesn’t just affect search engine optimization—it also enhances search summaries, Knowledge Panels, and Google Discover results. Structuring content around entities using schema markup, structured data, and entity extraction, website owners can improve their chances of appearing in relevant search results while ensuring their content aligns with user intent.
Entities vs. Keywords: Key Differences
While keywords are specific words or phrases users type into search queries, entities provide deeper context, helping search engines connect related concepts and understand intent beyond just word matching.
| Aspect | Keywords | Entities |
| Definition | Words or phrases users search for. | Concepts with unique attributes and relationships. |
| Focus | Matching exact words in a query. | Understanding the meaning and context behind queries. |
| Example | “Cute kitten video” | The concept of “cats” (a species, carnivorous animal, taxonomy, breed types, etc.) |
| Scope | Limited to language and phrasing. | Independent of language; globally recognized concepts. |
| Usage in SEO | Optimized through keyword placement and density. | Enhanced using structured data, entity research, and schema markup. |
| Search Engine Understanding | Identifies and ranks pages based on matching words. | Recognizes relationships between concepts through Google’s Knowledge Graph. |
| Impact on Search Results | Helps rank for specific search phrases. | Improves semantic search, influencing Knowledge Panels, Google Discover, and accurate search results. |
| Connection to Other Concepts | Standalone words; sometimes ambiguous. | Linked within an entity database, showing direct and indirect relationships. |
Here’s an example to understand this difference better, If you search for “cute kitten video,” search engines identify the keyword and match it to relevant web pages. But when Google recognizes “cats” as an entity, it can pull information about breeds, behavior, related searches, and even connect multiple meanings (e.g., pet vs. musical “Cats”).
Types of Entities in SEO
Entities in SEO are not just words but distinct concepts that search engines recognize and categorize to improve search accuracy. These entities can be classified into different types based on their characteristics and context.
1. Named Entities
These refer to specific names of people, places, organizations, or brands. Search engines recognize these entities and connect them to related knowledge panels and structured data.
- Example: Elon Musk, New York City, NASA, Tesla
2. Conceptual Entities
These represent abstract ideas rather than physical objects. Search engines categorize them based on semantic relationships and knowledge graphs to understand broader topics.
- Example: Sustainability, Artificial Intelligence, Democracy
3. Object-Based Entities
These entities include physical objects, products, or things that have a clear, identifiable presence. Google recognizes them through structured data markup and product-based knowledge panels.
- Example: iPhone 15, The Eiffel Tower, Toyota Camry
4. Event-Based Entities
These refer to historical or upcoming events that search engines track and organize in search results. Google’s Knowledge Graph often pulls details from news articles and authoritative sources.
- Example: Olympics 2024, Super Bowl LVIII, World War II
5. Digital Entities
These include web-based platforms, applications, or digital services that search engines categorize separately from physical objects.
- Example: Facebook, Google Drive, ChatGPT, Netflix
6. Medical & Health Entities
These entities cover health-related topics, diseases, treatments, and medical organizations. They are crucial for providing accurate search results, especially in Google Discover and health-related queries.
- Example: Diabetes, Mayo Clinic, WHO, COVID-19 Vaccine
7. Time-Based Entities
These represent specific time frames, dates, or historical periods that are used for search intent classification and event tracking.
- Example: Renaissance Era, December 25, 2023, Q4 2024
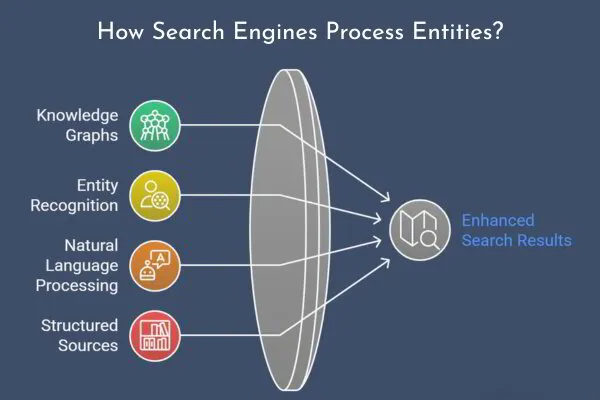
How Search Engines Process Entities?
Search engines like Google go beyond simply matching words; they identify, categorize, and connect entities to form a structured understanding of information. This process is driven by knowledge graphs, which map relationships between different entities and improve the accuracy of search results.
Instead of analyzing isolated words, search engines assess how entities relate to each other, making it easier to interpret user queries and refine search intent.
To identify entities, search engines extract data from structured sources like schema markup, Wikipedia pages, and authoritative databases.
By using natural language processing (NLP) and entity recognition, they determine whether a term represents a person, place, organization, or concept.
For example, when a user searches for “Leonardo da Vinci,” Google recognizes him as a historical figure rather than just a phrase and retrieves relevant information about his biography, artistic contributions, and scientific discoveries.
Once entities are identified, they are linked together within a knowledge graph. These networks of interconnected entities allow search engines to categorize information and improve contextual relevance.
If a search relates to Albert Einstein, for instance, Google automatically connects him to topics like the Theory of Relativity, Princeton University, and the Nobel Prize. By recognizing these relationships, search engines refine their understanding of topics, helping them differentiate between similar terms.
Entity Relationships and Context
Entities in SEO do not function in isolation; they exist within a web of connections that help search engines determine context and meaning. Rather than simply identifying words, search engines analyze how entities relate to one another, allowing for a deeper understanding of content.
These relationships enable search engines to refine search intent, categorize topics accurately, and present relevant search results that go beyond surface-level keyword matching.
For example, when a user searches for Barack Obama, search engines recognize the connections between him and related entities such as Michelle Obama, the U.S. Presidency, and the Affordable Care Act.
This means search results are not limited to a single webpage about him but may also include content about his policies, political impact, and public appearances. This interconnected approach ensures users receive contextually relevant information rather than isolated facts.
By mapping out these relationships, search engines improve their ability to distinguish between similar terms. A search for “Washington” could relate to a historical figure, a city, or a state.
Instead of relying solely on keyword matches, search engines assess semantic relationships between entities in SEO to present results that align with what the user is actually looking for.
Entity-Based SEO Implementation Strategies
Implementing entity-based SEO involves structuring content in a way that helps search engines understand, categorize, and connect entities more effectively. Rather than relying solely on keywords, this approach ensures that search engines recognize the relationships between concepts, improving search accuracy and visibility.
Entity identification and mapping is a foundational step in this process. It involves pinpointing key entities—such as people, places, organizations, and concepts—and defining how they relate to one another. This structured approach allows search engines to establish semantic connections between topics, leading to more precise search results.
For example, a webpage about digital marketing should highlight related entities like Google Ads, SEO strategy, and content marketing, reinforcing the topic’s depth and relevance.
One of the most effective ways to implement entity-based SEO is through schema markup. Using structured data provides search engines with explicit details about an entity, making it easier to categorize content.
When a webpage includes schema markup, it helps search engines recognize whether a term refers to a brand, concept, or product, reducing ambiguity and enhancing search rankings.
Entity-based internal linking is another critical strategy. Instead of linking to pages based purely on keyword anchors, internal links should connect related entities, reinforcing the contextual relationships between different topics.
A well-structured internal linking system guides search engines through a website’s content while improving user experience by directing visitors to relevant information.
Incorporating entity-based optimization into content strategies requires a shift from traditional keyword-focused SEO to a more context-driven approach. Pages should naturally integrate relevant entities alongside target keywords, ensuring that search engines capture the full meaning behind the content.
As search algorithms continue to evolve, focusing on entity optimization will be essential for improving search visibility, contextual relevance, and overall SEO performance.
How to Optimize Content with Entities?
Optimizing content for entity-based SEO requires structuring information to strengthen semantic relationships and enhance topical relevance.
A well-optimized content strategy begins with entity mapping. This involves identifying core entities relevant to a topic and organizing them in a way that search engines can interpret.
For instance, an article on digital marketing would not only include keywords like SEO and Google Ads but also related entities such as content marketing, PPC campaigns, and search engine algorithms. This structured approach signals relevance and authority to search engines, improving search rankings.
SEO tools like ChatGPT and Surfer SEO can assist in optimizing content by identifying entity n-grams, which highlight recurring patterns of related terms. These insights help in structuring content with entity-rich language, ensuring that search engines capture the broader meaning rather than just indexing isolated keywords.
Strategic internal linking further enhances entity optimization. Connecting pages that share common entities strengthen a website’s semantic structure, signaling to search engines that the site comprehensively covers a topic. This approach not only improves crawling efficiency but also boosts domain authority by reinforcing thematic relevance.
Integrating entity schema within content provides an additional layer of optimization. Nesting entity schema markup inside an article schema allows search engines to process structured data more efficiently.
Referencing authoritative sources like Wikipedia and Wikidata within schema markup helps search engines verify entity accuracy, making it easier to interpret complex topics, brand names, and abstract concepts.
Unlock the Full Potential of SEO with Entity Optimization
Entities have transformed SEO by shifting the focus from keyword frequency to context and relationships. Search engines now prioritize entity connections to deliver more relevant, accurate, and meaningful search results.
By structuring content around entities, implementing schema markup, and using internal linking strategically, businesses can enhance search visibility, improve user experience, and establish authority in their niche.
Adopting entity-based SEO isn’t just about improving rankings—it’s about ensuring that search engines fully understand your content and present it to the right audience. With search algorithms continuing to evolve, businesses that embrace entity optimization will gain a competitive edge, attracting more qualified traffic and achieving sustainable growth.
At Boba Digital, we specialize in data-driven SEO strategies that go beyond just keywords to maximize your online presence. Our proven approach has helped businesses drive leads, increase traffic, and maximize ROI through advanced entity-based SEO techniques.
Ready to take your SEO efforts to the next level? Schedule an appointment or contact us today to discuss how we can help your business thrive. Book a Consultation
FAQs
What tools can I use to identify and optimize entities on my website?
Tools like Google’s Natural Language API, Surfer SEO, and ChatGPT help analyze entity relationships, optimize content, and enhance semantic relevance for search engines.
How does Google’s Knowledge Graph relate to entity-based SEO?
Google’s Knowledge Graph maps out connections between entities, allowing search engines to provide contextually relevant search results instead of relying solely on keywords.
What role does schema markup play in optimizing for entities?
Schema markup provides structured data that helps search engines categorize entities accurately, improving search visibility and Knowledge Panel appearances.
Can optimizing for entities help with voice search results?
Yes, voice search relies on entity-based SEO to understand user intent, delivering more accurate and conversational results.
How does semantic search impact traditional keyword strategies?
Semantic search shifts the focus from exact-match keywords to entity relationships, improving search accuracy and content relevance.
What is the difference between entity matching and entity linking?
Entity matching identifies similar entities across datasets, while entity linking connects entities within content to enhance context and authority.