What Are Semantic Terms in SEO & Why They Matter for Rankings
Ever feel like search engines know exactly what you’re thinking, even when you type in a half-baked question?
That’s not magic — it’s a semantic search at work. Modern search engines have moved way past just matching individual keywords. They’re now all about understanding the deeper meaning behind user queries and figuring out what you really want.
Instead of obsessing over repeating a target keyword a dozen times, smart SEO today leans into context, user intent, and semantically related keywords. This approach helps your pages show up for real, human questions, not just robotic phrases.
Semantic SEO is transforming how your content gets discovered and how your website climbs search engine rankings.
Ready to see how semantic terms can push your content into the spotlight? Let’s uncover what makes semantic SEO so important.
What are Semantic Terms in SEO
When it comes to SEO, semantic terms are the words and phrases that expand on your main topic, making your content more meaningful and easier for search engines to understand.
Instead of focusing only on your primary keyword, semantic terms help you paint a bigger picture. They allow search engines to see the full context and better match your page with user queries that are similar in meaning, even if they do not include your exact keyword.
Imagine you are writing about “jaguar.” Without context, it could mean the animal, the car brand, or even a sports team. If your page also talks about “luxury cars,” “sedans,” or “British automotive,” it becomes clear you are referring to the car brand.
These related phrases act like clues, guiding modern search engines toward the right interpretation.
Semantic keywords are different from traditional keywords in a big way. Old SEO strategies often revolved around repeating a single keyword to signal relevance. While that might have worked years ago, search engines today are smarter.
They rely on semantic search to understand the deeper meaning behind each page. Instead of just matching exact words, they evaluate user intent and overall content quality.
This shift is why using semantically related keywords and related search queries has become so important. By naturally weaving in these terms, you show that your content is comprehensive and helpful. You are not just targeting one phrase but covering an entire topic in depth.
With semantic SEO, you move from simply chasing individual keywords to focusing on the entire story your content tells. This approach helps search engines provide better answers to user queries, improves your search engine rankings, and boosts your chances of appearing in featured snippets or knowledge graphs.
When you think beyond just keywords and start using related phrases, structured data, and internal linking, your pages start to shine in search engine results pages.
The Evolution of Search: From Keywords to Semantics
Think back to the early days of the internet, when websites felt like digital billboards crammed with the same words repeated over and over.
Back then, SEO was all about exact-match keywords. If you wanted to rank, you had to squeeze your target keyword into every sentence possible. The strategy worked, but it made the content dull and robotic.
This rigid approach opened the door to keyword stuffing and other shortcuts that focused on tricking algorithms instead of helping real people. Search engines would often rank pages high simply because they were overloaded with keywords, even if the content offered little actual value.
Then came a turning point. Google’s Hummingbird update flipped the script by introducing a focus on meaning rather than pure word matching. Suddenly, context and user intent started taking center stage.
The BERT update took it even further, allowing Google to understand natural language almost like a human would. These advancements made it possible to grasp the subtle differences in user queries and provide more accurate, helpful results.
With natural language processing and AI coming into play, search engines began to look at content through a new lens. They started connecting dots between related phrases, interpreting synonyms, and understanding the story behind every word on a page.
Just scanning for individual keywords, they began evaluating how a piece of content addressed the needs and questions of users.
Including semantically related keywords and related search queries keeps your content diverse and avoids the trap of keyword stuffing. It also helps maintain a natural flow, making your content feel more like a conversation than a mechanical list of phrases.
This evolution pushed SEO beyond simple tricks and forced businesses to focus on high-quality content that genuinely helps users. Now, it is less about playing the system and more about answering real questions, solving problems, and building trust.
How Semantic Terms Work in SEO
When a user types in a query, modern search engines break it down to understand keywords, related phrases, and the real intention behind the words.
Rather than sticking to simple matches, they look at how words and phrases relate to each other, uncovering the true context.
While scanning your content, Google uses natural language processing to read it almost like a human. NLP helps search engines figure out the meaning and tone of your page, not just individual terms. Entity recognition identifies important people, places, and organizations mentioned, while topic modeling groups your content into bigger themes.
This approach allows you to show your page for a wide range of related search queries, not just your main target keyword.
For instance, a page about “best budget travel tips” can also appear when someone searches for “cheap vacation ideas” or “affordable ways to travel.” Including semantic keywords and related phrases, you help search engines understand your content and match it to different types of user queries.
This understanding powers features like featured snippets, Knowledge Graph panels, and AI Overviews. These elements grab attention right on the search engine results pages, bringing more visitors to your site without them needing to click multiple links.
Using semantic SEO efforts, you can improve search engine rankings, boost user engagement, and create content that feels natural and complete. Techniques like structured data, internal linking, and a mix of related semantic keywords strengthen your pages even more.
Rather than focusing on individual keywords, a modern SEO strategy centers around creating high-quality content that answers questions and aligns with what people actually want.
Types of Semantic Terms
1. Synonyms and Closely Related Terms
Ever get tired of reading the same word repeated endlessly on a page? You are not alone. Readers (and search engines) want content that feels natural and easy to follow. That is where synonyms and closely related terms come into play.
Synonyms are alternative words or phrases that share similar meanings with your main keyword. They help you capture more user queries without making your content sound robotic. For example, if your target keyword is “affordable laptops,” words like “budget laptops,” “cheap notebooks,” and “low-cost laptops” keep your content fresh and engaging while addressing the same search intent.
Beyond synonyms, there are deeper relationships like hyponymy.
Think of “poodle” as a hyponym of “dog,” which is a type of “animal.” By using more specific or more general terms, you can widen the net of relevant search queries your content can catch.
Meronymy and holonymy also come into play, where one term describes a part of something larger. For instance, “keyboard” is a part of a “computer.” Including these related concepts shows that your content covers the topic thoroughly.
Relying on just one keyword can make your content feel forced and harm your SEO performance. Repeating the same phrase too often is known as keyword stuffing, and it can turn readers away while triggering search engine penalties.
To find the best synonyms and related terms, lean on tools like Google Trends, SEMrush, and Ahrefs. You can also look at competitor pages that rank high in search engine results and see what variations they use.
These strategies help you discover semantically related keywords and craft content that feels human and authentic.
2. Long-Tail Keywords and Natural Language Queries
Someone might ask, “What is the best laptop for video editing under a thousand dollars?” That question shows exactly how long-tail keywords work. These detailed, specific phrases capture a user’s real intent and match the natural way people search today, especially through voice commands.
Long-tail keywords reflect natural language and often sound like a conversation. Including question words such as “what,” “how,” and “why” helps your content appear in voice search queries and boosts your chances of being featured in snippets.
A major benefit of long-tail keywords is lower competition. While broad terms attract large audiences and high costs, specific phrases draw in users who are ready to act. This focus often leads to higher conversion rates and stronger connections with potential customers.
For those running paid campaigns, using long-tail keywords can also lower your cost-per-click. Broad keywords can be expensive because so many advertisers want them. More specific phrases usually cost much less, allowing you to reach a more targeted audience without overspending.
Keyword research tools such as SEMrush, Ahrefs, and even Google’s autocomplete and related searches help uncover valuable long-tail opportunities.
Exploring related search queries and checking top-performing competitor content can reveal phrases that match user intent and highlight gaps your content can fill.
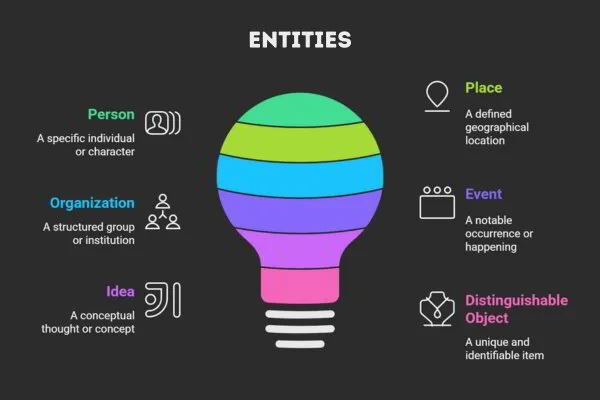
3. Entities (People, Places, Things, Concepts)
Scroll through any search results today, and you will see that search engines do more than match words.
They recognize the actual people, brands, places, and ideas woven into your content. These are known as entities. In SEO, entities act like anchor points that help search engines connect your page with the correct meaning and user intent.
When your content mentions well-known figures, companies, or locations, search engines use Named Entity Recognition (NER) to classify and understand these references. Mentioning “Mustang” on a page could point to a car or a horse.
Add context with words like “Ford,” “sports car,” or “engine specs,” and the search engine can confidently show your page to someone interested in vehicles rather than animals.
Bringing entities into your content does more than add detail. It shows search engines that your page covers a topic in a complete, trustworthy way. Using structured data gives these signals even more weight, helping your content appear in features like knowledge panels or rich results that stand out in search engine results pages.
SEO platforms such as InLinks, SurferSEO, and Clearscope offer tools to identify which entities strengthen your content. These services might cost anywhere from $79 to $300 each month, but they can guide you in shaping a strong semantic SEO strategy that truly reflects expertise and relevance.
Highlighting the right entities transforms your page from a simple keyword-focused article into a rich, informative resource.
4. Contextual Phrases and Topic Clusters
Strong SEO today is not just about single keywords floating on their own. The real power comes from building content that feels connected and complete. This is where contextual phrases and topic clusters make a huge impact.
Contextual phrases are words and supporting terms that add extra layers of meaning to your main topic. Rather than relying only on a target keyword, these phrases help search engines understand the depth and direction of your content. They show that your page addresses different angles of a subject, making it easier to match with varied user queries and related search intents.
Topic clusters take this idea further. A topic cluster strategy groups related content around one main “pillar” page, with each supporting page linking back to it. Think of a pillar page covering “local SEO strategies,” supported by detailed guides on “Google Business Profile optimization,” “local keyword research,” and “review management tips.”
When you organize content this way, search engines recognize the relationships between your pages. This structure signals that your site holds authority on that topic, boosting trust and helping improve your search engine rankings. It also enhances internal linking, guiding readers through a logical path so they stay longer and explore more.
Creating topic clusters also makes your website easier for Google to crawl and index. Once the search engine understands the semantic relationships among your pages, it can better showcase your content in search engine results and provide more relevant search results to users.
Building around contextual phrases and topic clusters transforms your website into a clear, informative hub. It supports a semantic SEO strategy, strengthens user experience, and positions your site as a go-to resource in your niche.
5. Semantic Relationships (LSI and Co-occurrence)
Words have a way of forming natural friendships. In SEO, these relationships reveal valuable insights into how topics connect and support each other.
This is where semantic relationships, including Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) and co-occurrence, truly shine.
LSI keywords refer to terms that frequently appear alongside your main topic, creating a fuller, more detailed picture for both readers and search engines. These words are not simple synonyms but rather companions that strengthen the message.
For example, an article about “healthy eating” might include phrases like “nutritious meals,” “whole foods,” “meal prep,” and “balanced nutrition.” Together, they help clarify the topic without relying on constant repetition.
Co-occurrence focuses on observing which words and phrases often appear together across different high-ranking pages. When search engines spot these patterns, they begin to understand which terms naturally support one another and how they build a topic’s context.
Seeing “vehicle,” “engine specs,” and “fuel efficiency” alongside “car” helps search engines understand content more accurately, even when certain keywords are not explicitly mentioned.
Spotting the right LSI and co-occurring terms starts with a careful look at top search results. Bolded words in snippets often hint at important supporting terms. Keyword research tools like SEMrush, Ahrefs, and free keyword research tools can also uncover helpful patterns and show which related semantic keywords belong in your content.
While LSI is not an official Google ranking factor, including these terms enriches your pages and shows that you have covered a topic thoroughly.
It helps align your content with related search queries, boosts semantic SEO efforts, and offers a better experience to your readers.
6. Attribute and Feature Terms
A simple search for “running shoes” might bring up thousands of results, but what people really want are “breathable running shoes for trail running” or “lightweight shoes with extra heel support.”
These extra details are where attribute and feature terms step in and make your content stand out.
Attribute and feature terms highlight the specific qualities, technical details, or unique characteristics of a product, service, or topic. In e-commerce, these words help guide users to exactly what they are looking for without the guesswork. Terms like “wireless,” “scratch-resistant,” “sugar-free,” “vegan,” or “moisture-wicking” give content more depth and speak directly to user needs.
Including these descriptive terms ensures your content matches more detailed search queries and reaches users who are ready to take action. For example, someone searching for “ergonomic office chair with adjustable lumbar support” is likely far along in their buying journey and wants a precise solution.
When your content includes these attributes naturally, it increases the chance of ranking for transactional searches and attracting high-intent visitors.
These terms do more than help with organic rankings. In paid campaigns, using detailed attributes often means lower cost-per-click and higher ad relevance scores because the audience is more targeted.
Pages that include rich attribute details can show up for more long-tail keywords and related search queries, pulling in qualified traffic rather than broad, less interested clicks.
Beyond boosting rankings and clicks, this strategy builds credibility. Users feel more confident and informed when they see exact product features laid out clearly.
Search engines appreciate this clarity too, rewarding content that matches user intent and offers complete, high quality information.
7. Topical Categories and Broader Concepts
A website without clear topics can feel like wandering through a giant store with no signs.
You might stumble onto something interesting, but finding exactly what you need is frustrating. That’s why organizing content into topical categories and broader concepts is so important.
Topical categories act as the backbone of your content strategy. They represent overarching themes that tie together related pieces of content, helping both users and search engines understand what your site is really about.
Grouping articles, guides, and resources under strong categories signals to search engines that your site holds authority in those areas. This boosts your chances of ranking for related search queries and supports your semantic SEO strategy.
Addressing broader concepts within each category ensures your content feels complete and interconnected. For example, a health website might have categories like “nutrition,” “fitness,” and “mental wellness,” each covering various subtopics and answering different user queries.
This structure makes it easier for search engines to crawl and index your pages, improving your chances of appearing in search engine results pages for a wide range of relevant keywords.
Mapping content to these categories also strengthens internal linking. When your articles connect naturally within a category, visitors spend more time exploring your site, and search engines can better understand how each piece supports your overall topical authority.
For larger websites, keeping this structure organized is crucial.
Content management systems (CMS) and SEO plugins make it easy to assign categories, manage hierarchies, and maintain a clear site architecture. Many of these tools are free or affordable, so building a strong internal structure does not have to break the budget.
Semantic Terms vs. Traditional Keywords
| Feature | Semantic Terms | Traditional Keywords |
| Main Focus | Emphasizes context, meaning, and overall topic understanding | Targets exact words or phrases only |
| User Intent | Covers a wide range of related queries and intentions | Limited to specific, often narrow searches |
| Content Approach | Encourages thorough, well-rounded content that explores a topic deeply | Usually focused on surface-level keyword repetition |
| Example | Using “espresso machine” to support “coffee brewing” topics and related searches | Sticking strictly to “coffee brewing” only |
How to Find Semantic Terms
Google Features (People Also Ask, Related Searches, Autocomplete)
Finding the right semantic terms is like uncovering hidden gems scattered all over Google. While it might sound complicated, some of the best tools are already right in front of you — and they are free.
Start with Google’s autocomplete. As you type your seed keyword into the search bar, you will notice suggestions filling in below. These phrases come directly from real user searches, which means they reflect what people are actually looking for.
They can help you discover new angles, related phrases, and questions worth addressing in your content.
Another goldmine is the “People Also Ask” box that often appears near the top of search results. This section shows common questions tied to your keyword, revealing what users want to learn next.
By answering these questions in your content, you improve its relevance and increase your chances of capturing voice search queries and appearing in featured snippets.
Scroll down to the bottom of the search results page, and you will find “Related Searches.” These links highlight additional terms and variations that users explore after searching your main topic.
Adding these phrases to your content helps cover more ground and match a wider range of user queries.
Combining insights from autocomplete, People Also Ask, and Related Searches gives you a strong foundation of semantic keywords and supporting phrases. It turns your content from a single-focused piece into a comprehensive resource that helps search engines understand the full picture.
These simple steps guide your keyword research without the need for expensive tools. When you incorporate these semantic terms naturally, you build high-quality content that feels helpful and speaks directly to user intent.
Utilizing Keyword Research Tools for Semantic Analysis
Platforms like Semrush, Ahrefs, Moz, and Google Trends provide a treasure trove of data beyond just search volume.
You get insights into keyword difficulty, competition levels, and even how certain terms trend over time. With this information, you can identify high-potential semantic keywords that match your content goals and speak directly to user intent.
The process often starts with entering a seed keyword into one of these tools. From there, you can explore related search queries, discover semantically related keywords, and see which terms competitors are using effectively.
Studying top-ranking pages helps uncover the context and supporting phrases that help them perform so well in search engine results pages.
Google Trends, which is free, allows you to track how interest in certain topics changes over time. Meanwhile, more advanced platforms like Semrush and Ahrefs provide detailed competitive analysis and offer extensive lists of related semantic keywords.
These premium tools typically cost between $100 and $200 per month but deliver deep insights that can transform your content strategy.
Using these tools not only helps you find related semantic keywords but also gives you a clearer understanding of user intent and potential gaps in your current content.
When you combine this approach with your internal SEO strategy and strong on-page optimization, you build comprehensive, high-quality content that resonates with both search engines and real people.
Incorporating semantic analysis through keyword research tools ensures that your pages cover more ground, stay competitive, and provide genuine value.
Topic Modeling and Content Clustering
Topic modeling might sound technical, but at its core, it is about understanding which ideas naturally belong together.
It helps uncover connections between different terms and shapes your content around those relationships. Instead of obsessing over a single phrase, you explore the broader conversations your audience actually cares about.
Content clustering is where strategy meets structure. You start with a main pillar page, such as “email marketing,” which acts as the central anchor. Supporting pages branch out into related subjects like “email automation workflows,” “split testing subject lines,” or “boosting click-through rates.”
Linking these subtopics back to the main pillar creates a unified web of content that is both user-friendly and search engine-friendly.
For search engines, this interconnected design acts as a clear signal that your website covers a topic comprehensively. As a result, your site stands a better chance of being recognized as an authority, making it more visible in search engine results and more attractive to visitors looking for detailed, high quality content.
Tools like MarketMuse or Clearscope to handle this process automatically. These platforms analyze your existing content, spot gaps, and suggest new angles to strengthen your topical coverage.
While they can cost anywhere from $79 to $170 per month, they save time and bring valuable insights. On the other hand, manual clustering is just as effective for those who want more control or have a tighter budget.
A strong content cluster does more than improve rankings. It guides visitors deeper into your site, builds trust, and helps establish your brand as a go-to resource.
Using topic modeling and clustering, you transform scattered articles into a cohesive system that delivers a better experience and keeps people engaged longer.
How to Use Semantic Terms
Incorporating semantic terms in content
Writing content that feels smooth while still attracting search engines is all about balance. Semantic terms help you achieve this by adding depth without forcing awkward repetitions.
Start by including semantic keywords naturally, focusing on meaning and context rather than squeezing them in everywhere. Break your content into clear sections with subheadings that explore related topics.
For example, a page on “local SEO” might cover “Google Business Profile tips” and “customer review strategies,” signaling thorough coverage to search engines.
Skip keyword stuffing — it makes your writing clunky and can hurt rankings. Instead, think about how you’d explain the topic to a friend, using a mix of phrases that keep it natural and easy to follow.
Done right, semantic terms strengthen your content, improve rankings for related queries, and help build trust with your audience.
Internal linking with semantic anchor texts
Internal links act as the roads that guide visitors from one point to another, and the anchor texts are the street signs that tell them exactly where they’re going.
Using descriptive, context-rich anchor text connects related pages in a way that feels natural for readers and clear for search engines.
Rather than using vague phrases like “click here,” opt for anchor text that describes the linked content, such as “local SEO tips for small businesses” or “email automation strategies.” This helps search engines understand the relationship between pages and strengthens your overall semantic SEO strategy.
Semantic anchor texts do more than improve navigation. They signal topical authority, show how your content pieces fit together, and make it easier for search engines to rank your pages for relevant search queries.
A smart internal linking approach improves user experience and builds a stronger, more connected content network that supports higher search engine rankings and keeps visitors exploring your site longer.
Using structured data and schema markup
When search engines scan your site, they need clear clues to understand every detail. Think of schema markup as the translator that turns your content into a language search engines read fluently.
Adding structured data helps connect the dots between different elements on your page.
With schema, you can show how a product relates to its reviews, pricing, and availability. This extra layer of context not only improves search engine understanding but also increases your chances of earning rich snippets, those standout search results that grab attention and boost click-through rates.
The best part? Many website plugins and tools make adding schema simple, often without any added cost. Whether you’re highlighting event details, product specs, or article metadata, schema markup supports your semantic SEO efforts by clarifying how your content serves user intent.
Using structured data transforms ordinary listings into detailed, eye-catching results. It strengthens your content’s connection to user searches, builds trust, and ultimately helps drive more qualified traffic to your site.
Why Semantic Terms are Crucial for SEO Success
Enhancing content relevance and depth
Using semantic terms helps you build content that feels complete and authoritative.
By covering related phrases and deeper concepts, you address a wider range of user questions and show search engines that your page offers real expertise. This depth signals to algorithms that your site deserves a top spot, boosting your chances of ranking for more related search queries.
When you focus on semantic terms, your content evolves from a basic keyword match to a resource that users and search engines trust.
It keeps visitors engaged longer, encourages them to explore more, and positions your brand as an industry leader.
Improving search visibility and rankings
Semantic optimization helps your content appear for multiple related queries, not just one exact phrase.
When your page covers topics in a broad, meaningful way, it increases the chance of ranking for long-tail keywords, related search queries, and even voice search queries.
This strategy also boosts your chances of landing in rich results like featured snippets, knowledge panels, and other AI-powered SERP features. By helping search engines understand the full context of your content, you make it easier for them to highlight your pages in more places, driving higher visibility and more clicks.
Semantic SEO turns your content into a powerful magnet, pulling in a wider range of searches and connecting you with more potential customers.
Aligning content with user intent
Nothing turns visitors away faster than content that feels off-target. When a page doesn’t deliver what someone expects, they quickly click out, which can hurt your credibility and search performance.
Semantic terms help you shape content that matches real questions and needs. Rather than focusing narrowly on a single keyword, you can explore all the related angles and topics your audience cares about. This approach creates a more complete, helpful resource that truly answers what people came to find.
When users find exactly what they need, they tend to stay longer, engage with more pages, and view your brand as a trustworthy source. This improved engagement not only builds stronger relationships with visitors but also signals to search engines that your content deserves higher visibility.
Aligning with user intent isn’t just about attracting clicks — it’s about keeping attention, building trust, and turning casual readers into loyal followers.
Supporting authority and topical expertise
Standing out online takes more than simply publishing content — it requires proving that you know your stuff. This is where semantic coverage makes a real difference.
When you address a topic in detail using related terms, questions, and supporting concepts, your site starts to look like an expert resource rather than just another blog. This level of depth signals to both readers and search engines that your content can be trusted.
Google’s E-E-A-T guidelines (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) reward this approach. A page that fully explores a topic and answers a wide range of related queries shows true expertise and builds authority in your niche.
This strategy improves rankings and builds credibility with your audience. Visitors are more likely to return, share your content, and view your site as a go-to source. Covering topics semantically helps you earn that trust and stay ahead in a competitive search landscape.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Relying solely on exact match keywords
One of the easiest traps to fall into with SEO is obsessing over exact match keywords. At the same time, they might seem like the safest bet, but relying on them alone can actually hold your content back.
Focusing only on exact keywords narrows your reach and misses the bigger picture of what users are really searching for. People phrase questions in countless ways, and sticking rigidly to one version means you lose out on valuable traffic from related search queries.
Adding semantic keywords and related phrases allows you to connect with a wider audience and capture different variations of search intent. It also helps your content feel more natural and engaging, rather than forced or repetitive.
Breaking free from the exact match mindset opens up new opportunities, improves your content’s depth, and positions your pages to perform better in modern search engine results.
Ignoring user intent and context
You can have all the keywords in the world, but if your page misses what people actually need, it won’t keep them around for long.
Ignoring context often leads to high bounce rates and weak engagement. Visitors arrive looking for specific solutions or clear guidance, and when they don’t find it, they click away in seconds.
Using semantic search strategies helps align your content with real user intent and context.
Including semantically related keywords and addressing related search queries ensures your content feels complete and genuinely helpful.
This approach strengthens user trust, keeps people engaged longer, and shows search engines that your page deserves higher search engine rankings.
Overusing semantic terms unnaturally
It’s tempting to think that sprinkling in as many semantic keywords as possible will supercharge your rankings. But stuffing your content with these terms can do more harm than good.
Overusing semantic terms disrupts the natural flow of your writing and makes it feel forced or robotic. Readers pick up on this immediately, and search engines do too.
Trying too hard to cover every possible variation or related search query can hurt readability and even lead to search penalties.
A strong semantic SEO strategy depends on balance. Integrate semantically related keywords in a way that feels smooth and genuinely supports the topic. Prioritizing user-first writing keeps your content engaging, trustworthy, and easier to rank.
Conclusion
Mastering semantic terms is like switching from a flashlight to a floodlight — you stop focusing on one tiny spot and start illuminating the whole picture.
By enhancing content relevance and depth, boosting search visibility, aligning with true user intent, and supporting E-E-A-T, you set your site up for real, lasting success.
Using semantic SEO not only helps you climb rankings but also builds stronger topical authority and keeps visitors engaged. When your content feels complete and genuinely helpful, both search engines and users reward you for it.
Ready to move beyond keywords and turn your website into a trusted, high-ranking powerhouse? The team at Boba Digital can help you craft a strategy that’s sharp, future-proof, and designed for growth.
Let’s make your content the one that answers questions before they’re even asked. Contact Boba Digital today — your next big leap in search results is just a click away.
FAQs
How do semantic terms differ from traditional keywords?
Semantic terms focus on context and meaning rather than exact word matches. While traditional keywords aim to match specific phrases, semantic terms include related words and concepts that help search engines understand the bigger picture of your content. This approach allows you to cover a topic more thoroughly, match a wider range of user queries, and better address search intent, leading to stronger rankings and a more natural reading experience.
What role do entities play in understanding semantic terms?
Entities — like people, places, brands, and concepts — act as anchors that help search engines interpret the true meaning of your content. When you mention entities clearly and accurately, search engines can connect your content to broader topics and user queries more effectively. Including relevant entities improves your topical authority and helps your content appear in rich results, like knowledge panels or featured snippets, boosting your visibility and credibility.
Are Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) keywords the same as semantic terms?
Not exactly. LSI keywords are terms that often appear together in related documents and help clarify meaning, but they’re only one piece of the semantic puzzle. Semantic terms include LSI keywords plus synonyms, related phrases, and contextual words that reflect user intent. While LSI helps support understanding, focusing on a full range of semantic terms gives your content depth and helps it perform better across a wider range of search queries.
How can I identify relevant semantic terms for my content strategy?
Start with tools like Google’s autocomplete, People Also Ask, and related searches to see what real users are looking for. Keyword research platforms like Semrush, Ahrefs, and Moz can also uncover semantically related keywords, entities, and user questions. Analyzing competitor content and top-ranking pages can reveal gaps and opportunities. Once you gather this data, weave the terms naturally into your content to create a comprehensive and user-focused resource.
Do semantic keywords help with voice search optimization?
Yes, absolutely. Voice search queries tend to be longer and more conversational, reflecting how people naturally speak. Using semantic keywords and related phrases helps your content align with these natural language patterns. When your pages address specific questions and include conversational terms, they become more likely to appear in voice search results and featured snippets. This approach improves your chances of capturing valuable traffic from users searching hands-free on mobile and smart devices.